Anxiety is correlated with changes in breathing patterns. These changes can be for the worse or better depending on what you do to manage anxiety and stress. Learning how to relax with breathing techniques is an important step towards managing your anxiety.
Breathing is linked to both relaxation and anxiety.
When we breathe in our sympathetic nervous system is activated, and when we breathe out our parasympathetic nervous system is activated. Our sympathetic nervous system is our fight-or-flight system while our parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for relaxation.
Breathing techniques can help to trigger the relaxing, calming effect of our parasympathetic nervous system and reduce anxiety. By learning how to control your breath, you can learn how to better manage anxiety.
There are two types of breathing that can occur.
Diaphragmatic (abdominal) breathing is a type of deep breathing that engages your diaphragm and allows your lungs to expand and is associated with relaxation. Thoracic (chest) breathing, on the other hand, comes from your chest and involves short, rapid breaths, and is associated with anxiety.
There are many different breathing techniques that you can use to stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system to relax:
Belly Breathing
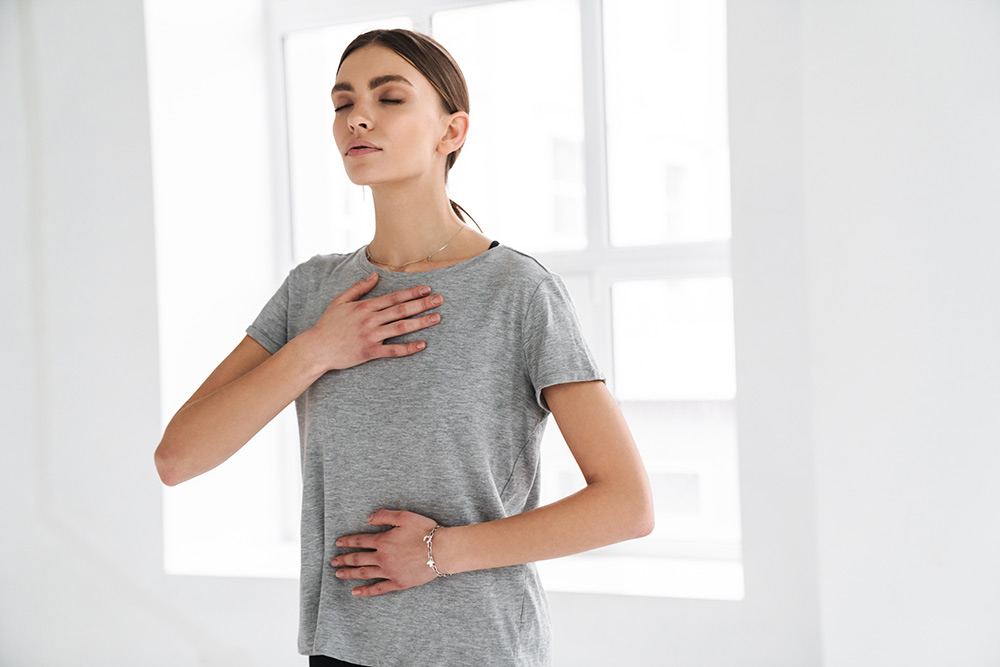
Shallow breathing contributes to anxiety. When people are anxious, they tend to take short, shallow breaths. Breathing in this way selectively activates the sympathetic nervous system and contributes to anxiety symptoms. Belly breathing (or deep/abdominal breathing) stimulates the relaxation response of our parasympathetic nervous system, which can help reduce your anxiety symptoms.
To do belly breathing, sit or recline in a comfortable position with your spine straight. Place one hand on your stomach and one on your chest. Breathe in through your nose so that you can feel the hand on your stomach rise and the one on your chest remain still.
As you breathe out, push all of the air out until you have completely emptied your lungs after which point an inhale will naturally occur. Try to make each breath last for at least six seconds. This breathing technique is meant to help you focus on your breath and breathe from your diaphragm rather than from your chest.
Box Breathing
Box breathing is a type of paced breathing. Paced breathing involves breathing at a set rate, which can help to calm and focus you. It’s simple to learn and practice and can help with stress management.
- Exhale to a count of four.
- Hold your lungs empty to a count of four.
- Inhale to a count of four.
- Hold the air in your lungs to a count of four.
- Exhale and begin the cycle again.
Relaxing Breath
The relaxing breath (or 4-7-8 breathing) is another type of paced breathing and works by engaging your parasympathetic nervous system longer than your sympathetic nervous system, triggering your body’s relaxation response.
- Inhale for a count of four.
- Hold your breath for a count of seven (optional).
- Exhale through your mouth for a count of eight and repeat the pattern.
Resonant Breathing
Resonant breathing (or coherent breathing) is another type of paced breathing that can help you reduce anxiety and get into a relaxed state.
- Inhale through your nose for a count of six.
- Exhale for a count of six and repeat the cycle.
Pursed-Lips Breathing
Pursed lips-breathing can help to make your breaths slower and more intentional.
- Inhale slowly through your nose (with your mouth closed) for a count of 2.
- Exhale through your mouth with pursed lips for a count of 4 and repeat.
Mindful Breathing
Mindful breathing is a type of breath awareness. When we’re mindful, we focus our attention on the present moment and allow thoughts to come and go without judgment. This can be helpful when you’re feeling overwhelmed or anxious as it allows you to focus on something else other than your anxiety.
To practice mindful breathing, sit in a comfortable position and focus your attention on the rise and fall of your breath without trying to change it. Start with ten minutes a day, adding more time as you feel comfortable or as needed.
While the cause of anxiety can differ from person to person, breathing techniques can help reduce the symptoms of anxiety for everyone.
Intentional, slow, deep breathing is beneficial for those experiencing anxiety. The techniques found here can help you achieve relaxation and calm while lowering your stress levels. Give each a try to see which works best for you.